Every other year, in odd-numbered years, I conduct the Utility Fee Survey. This survey was designed to research what fees utilities charge, how much they charge for each fee, and to see what trends, if any, are occurring with fees. Here are links to previous Utility Fee Surveys:
2015 Utility Fee Survey Results
2017 Utility Fee Survey Results
2019 Utility Fee Survey Results
2023 Utility Fee Survey Results
The Utility Fee Survey alternates years with the Utility Staffing Survey, which is conducted in even-numbered years. Below are the results of the 2021 Utility Fee Survey.
Demographics of survey respondents
142 utilities (a 5.6% increase from 2019), representing 23 states (a 4.5% increase from 2019), ranging in size from 31 to 285,000 active accounts participated in the survey. Click on the links below to see charts of the various demographic data:
Size of participating utilities
Size of participating utilities under 20,000 accounts
Services provided by responding utilities
Positions of individuals completing survey
Tap fees and impact fees
The survey started with water and sewer tap and impact fees. There are some key distinctions to bear in mind when comparing tap and impact fees.
Tap fees should recover the cost of making the actual water or sewer tap. This includes direct costs such as labor, materials, and vehicle use as well as any indirect costs associated with completing the tap. Tap fees are classified as operating revenues.
Impact fees, sometimes called availability fees or system development charges, are designed to cover the incremental capital cost of adding an additional user to the water or sewer system. Impact fees are classified as non-operating revenues.
For utilities charging an impact fee based on number of bedrooms, monthly or daily usage, square footage, or lot size, I assumed three bedrooms or 3,000 gallons per month or 1700 square feet or one-quarter of an acre. Residential water tap fees charged by utilities responding to the survey range from $37.00 to $16,669.00 as shown below (clicking on the any of the graphics will open a larger image in a new window):
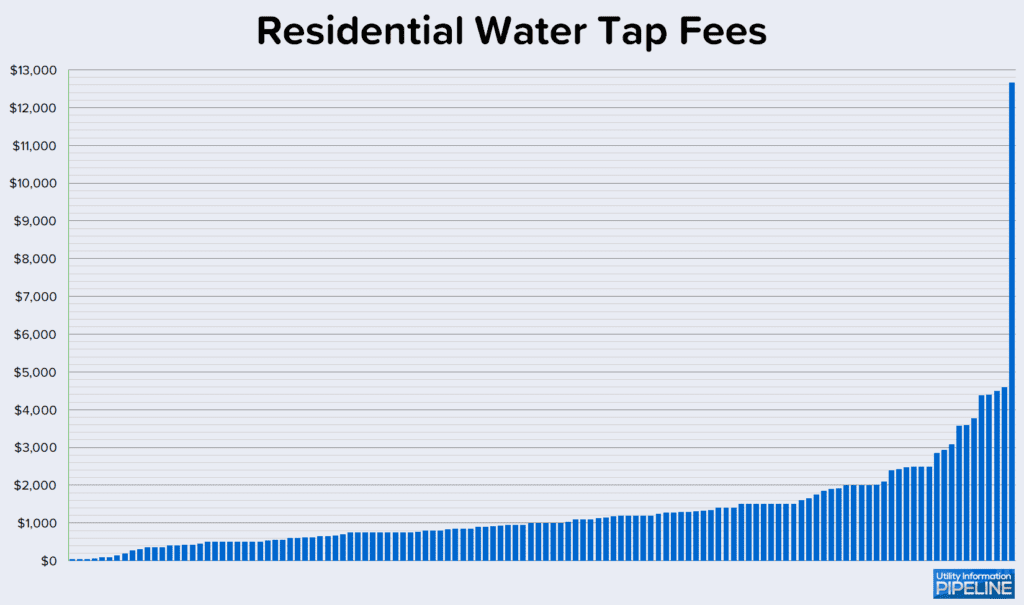
One other utility charges based on the time and materials cost incurred for a residential water tap at actual cost.
Utilities responding to the survey charge residential sewer tap fees ranging from $50.00 to $17,738.00 as depicted by this graph:
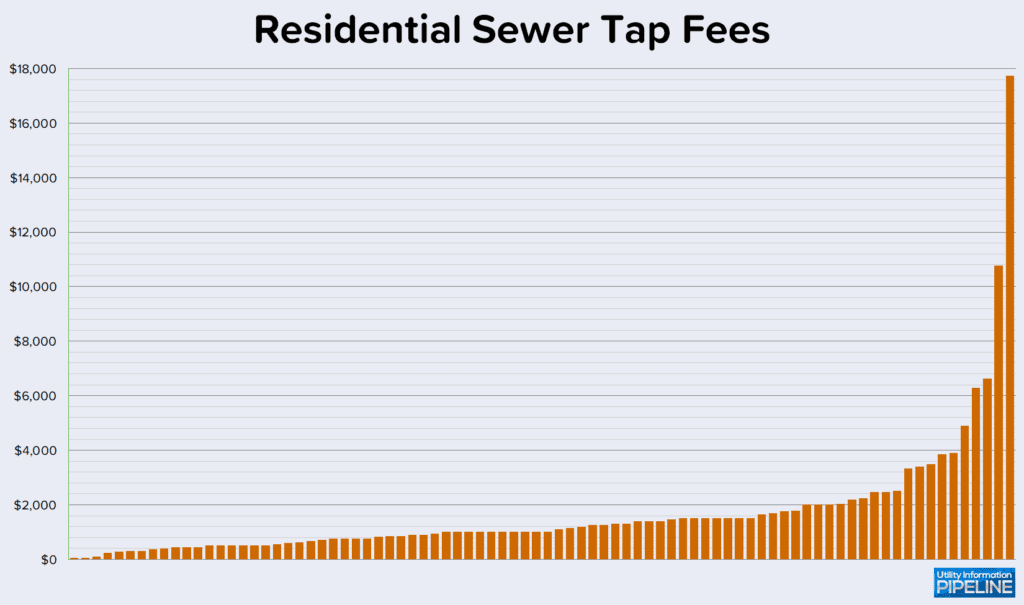
One additional utility charges the actual time and materials cost incurred for a residential sewer tap.
Residential water impact fees charged by utilities responding to the survey range from $16.00 to $6,381.00 as shown in this graph:
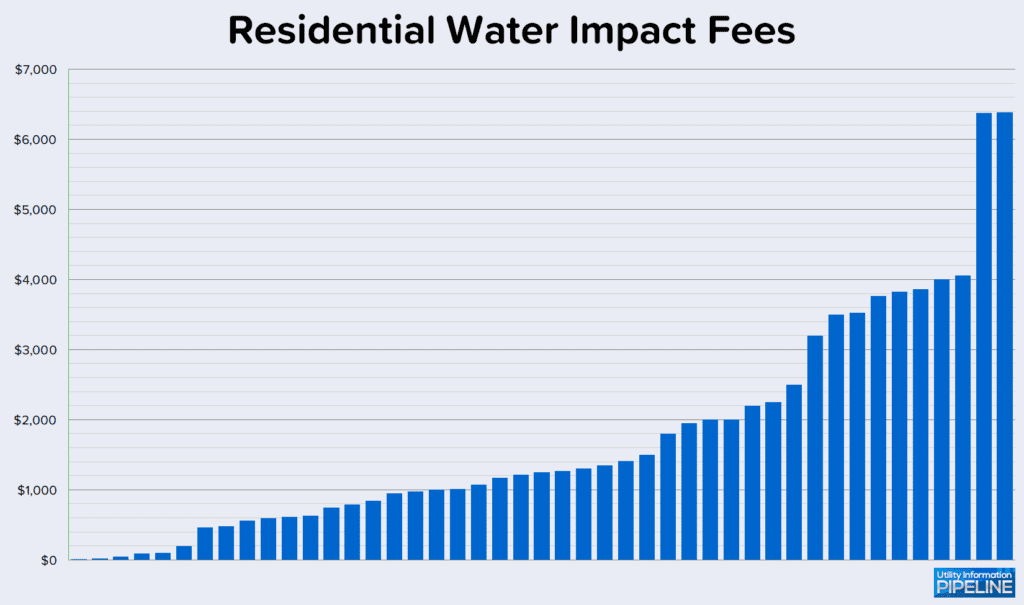
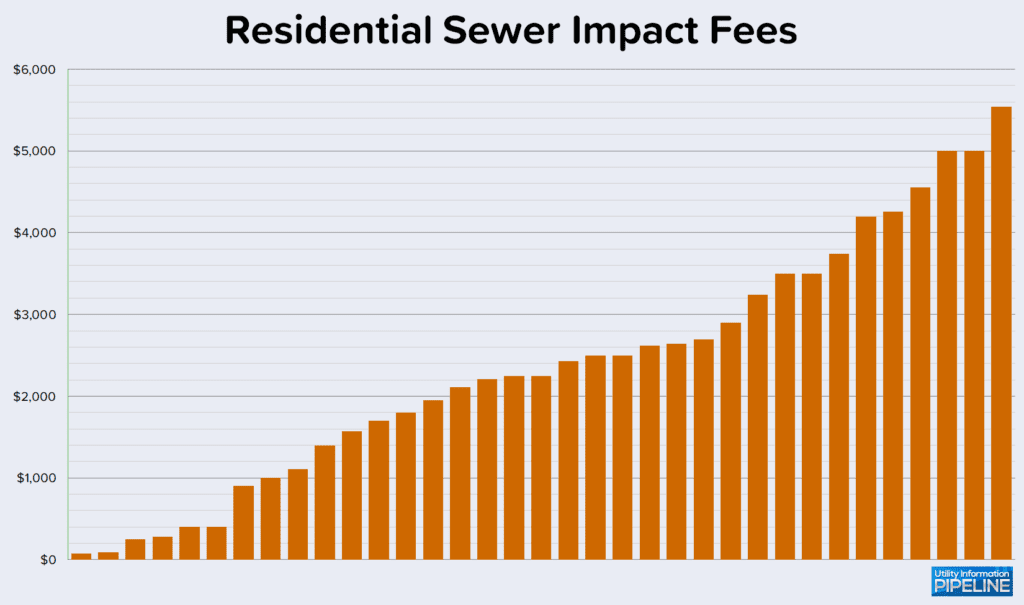
Utilities responding to the survey charge residential sewer impact fees ranging from $75.00 to $5,540.00 as shown here:
Late fees
Of the 142 participating utilities, 140 charge a late fee. As shown by this graph, charging a late fee as a percentage of the bill is the most popular method (clicking on the any of the graphics will open a larger image in a new window):
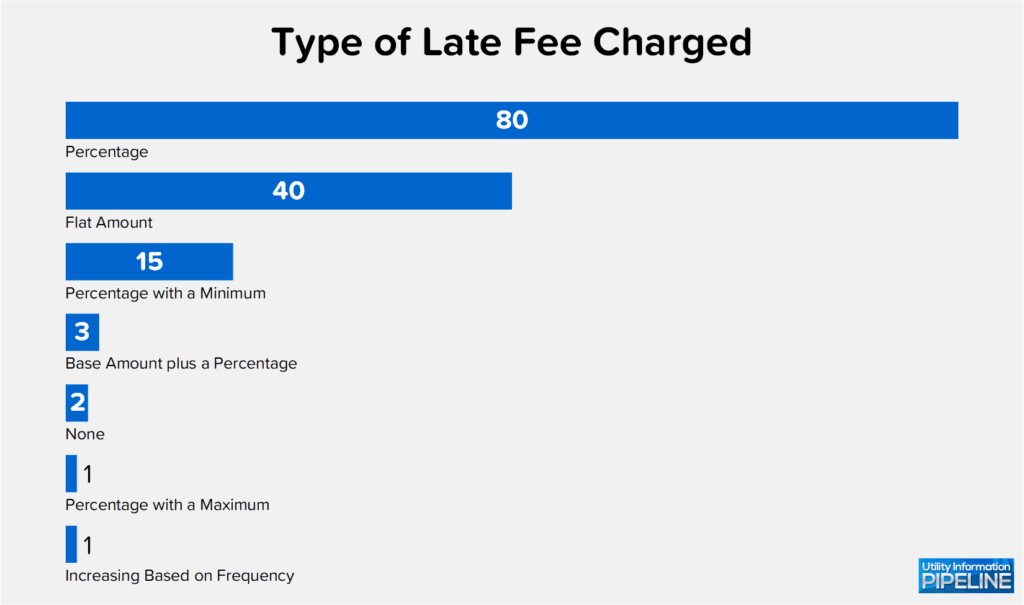
Compared to the 2019 Utility Fee Survey, utilities charging a percentage has increased (57.1% vs. 52.6%), and those charging a flat amount is up slightly (28.6% vs. 27.8%). The area that saw a decrease is with utilities charging something other than a percentage or flat amount (down from 19.5% to 14.3%).
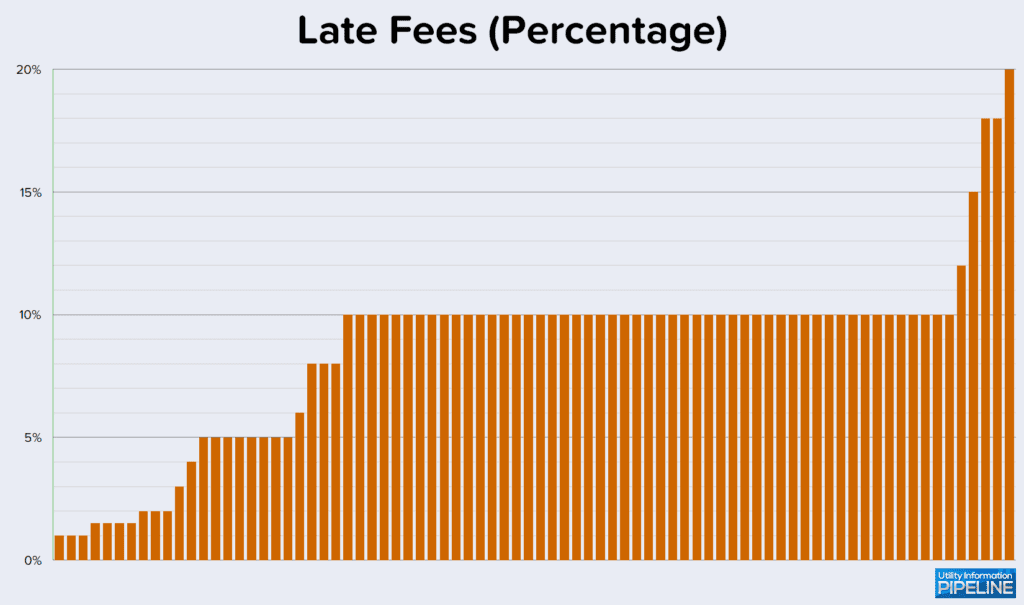
Utilities that assess a late fee as a percentage charge from 1% to 20%, with 10% again, by a wide margin, the most popular, as this graph depicts:
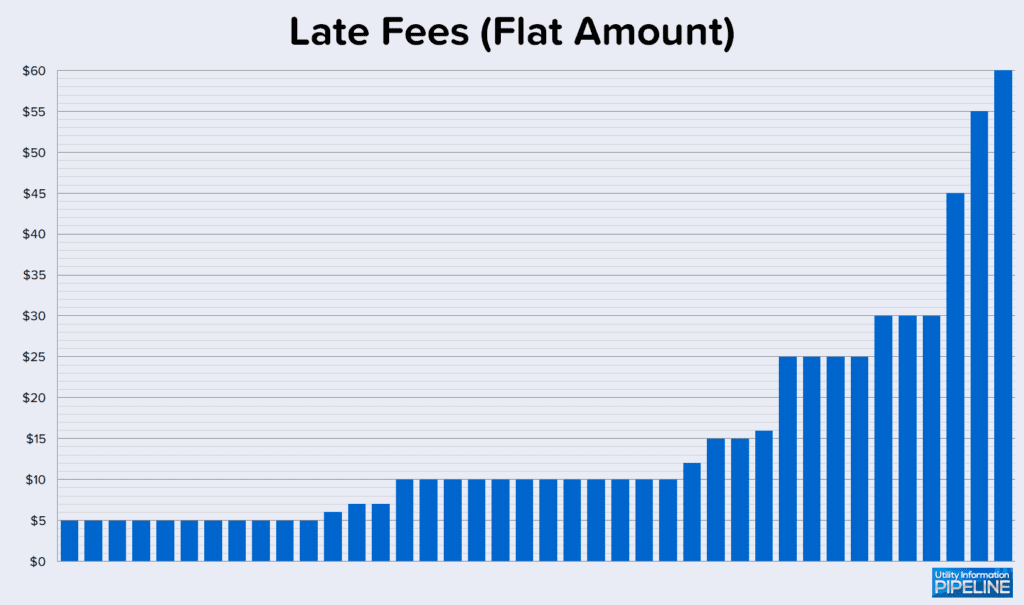
Late fees range from $5.00 to $60.00 for utilities charging a flat amount. This graph illustrates the late fee flat amounts:
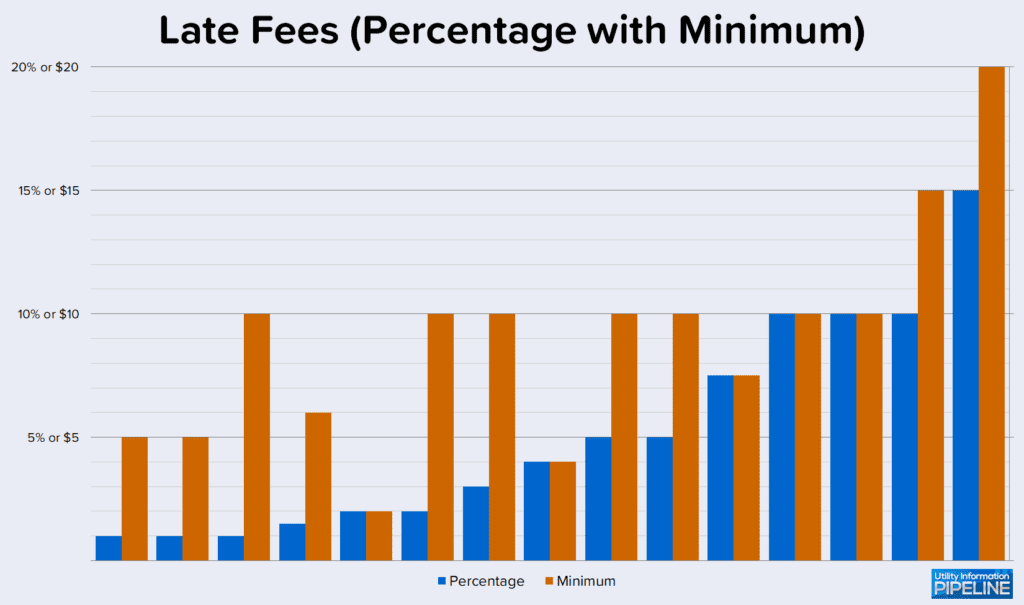
Fifteen of the utilities (up from 13 in 2019, a 15.4% increase) charge a hybrid late fee – a combination of a percentage with a minimum amount. Here is a graph showing what they charge:
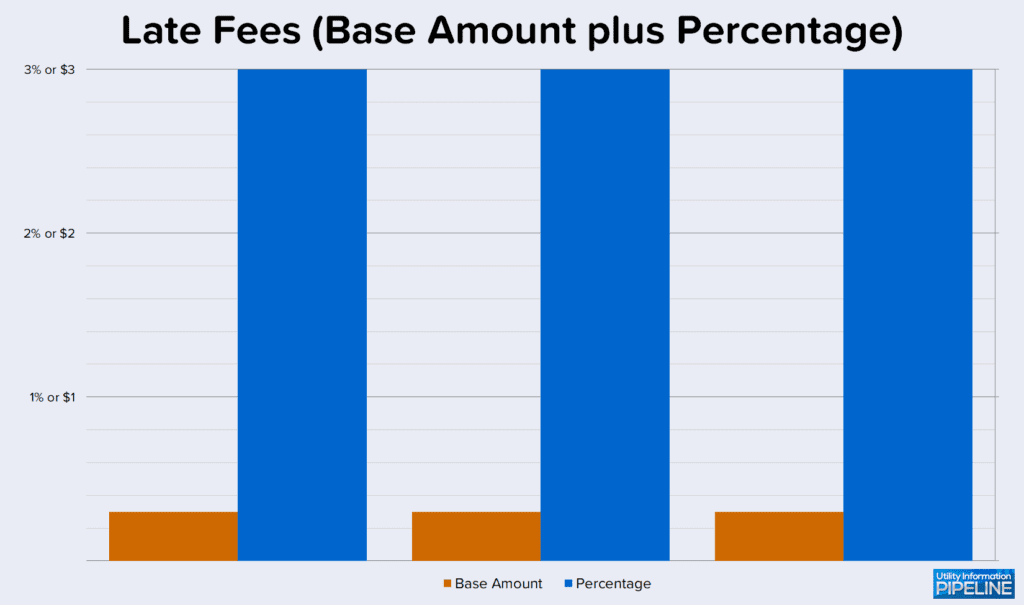
Three utilities charge a base amount plus a percentage as shown below:
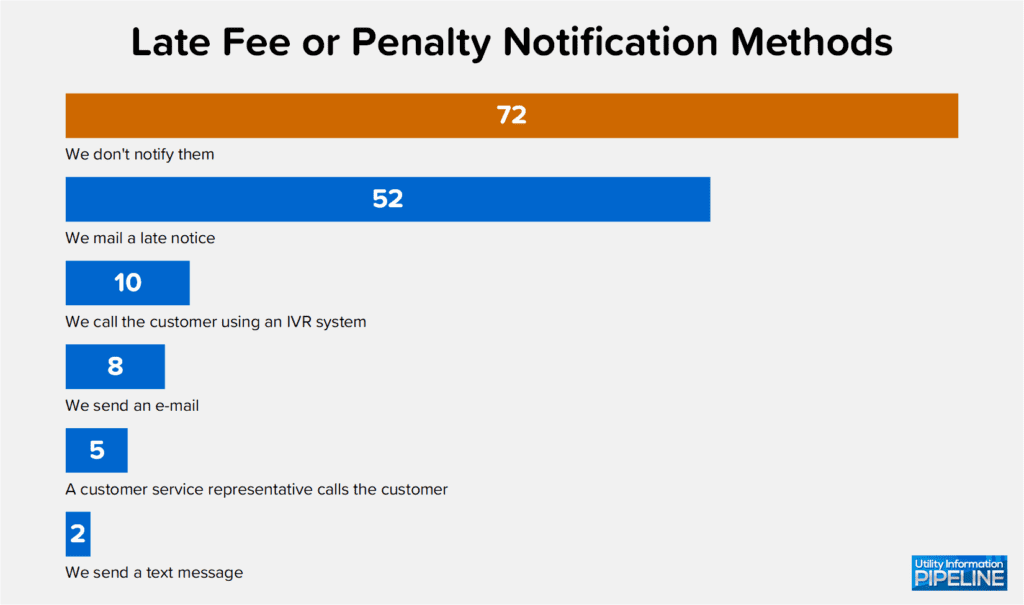
While not technically a fee, this year’s survey again asked how, other than the utility bill, each utility notifies customers that a late fee or penalty has been applied. Here are the responses to that question (the total of all responses is greater than the number of participating utilities because some utilities use multiple methods of contact):
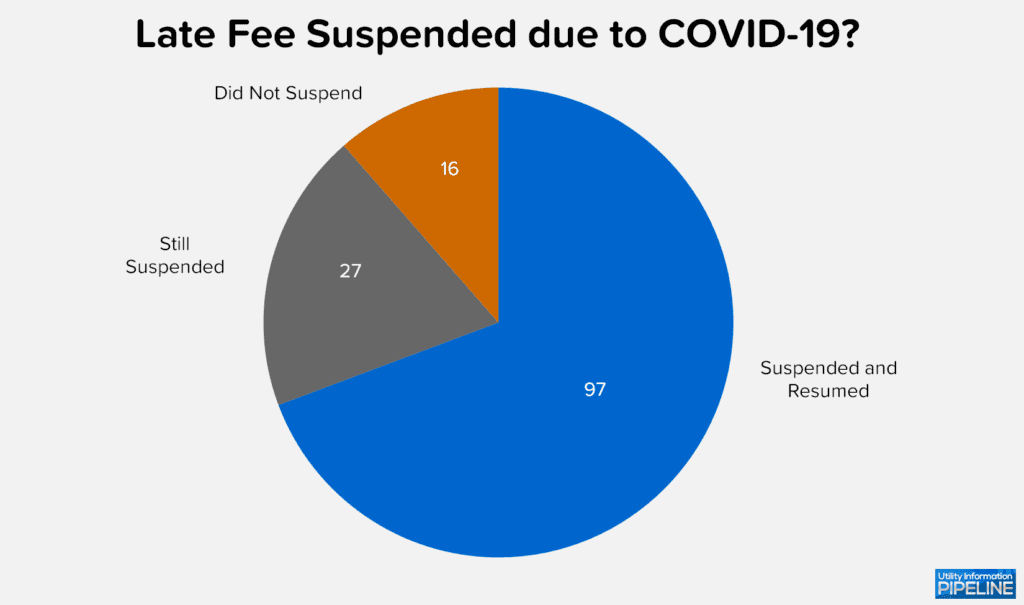
This year’s survey also asked if utilities suspended late fees due to COVID-19 and, if they did, have they resumed charging the late fee. Here are the results from that question:
Cut-off fees
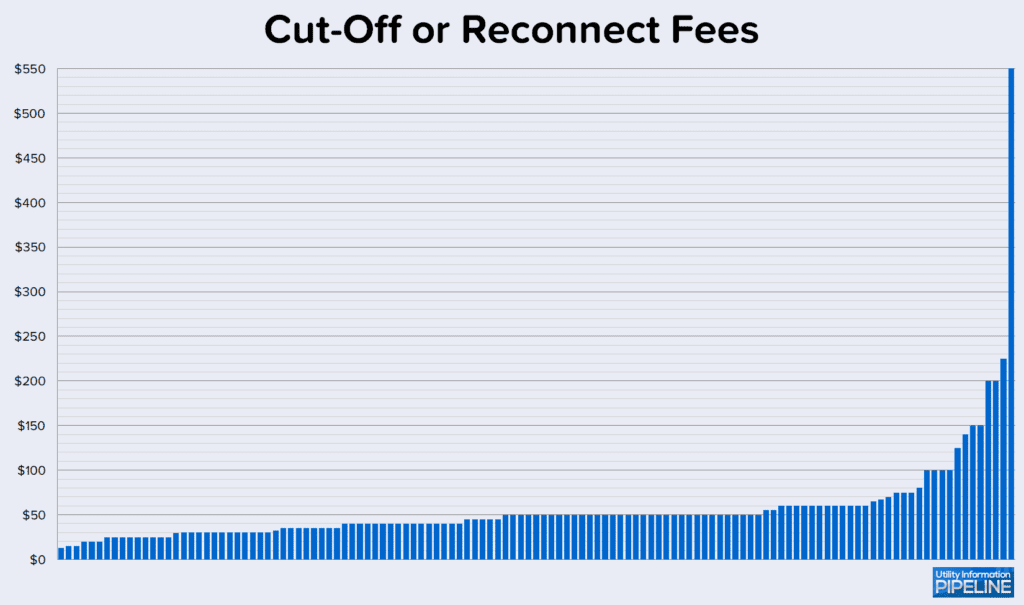
Thirteen of the 142 utilities do not cut off for non-payment. The remaining 129 that do cut off for non-payment all charge a cut-off or reconnect fee as a flat amount. Two of the responding utilities charge an escalating cut-off fee whereby the more times a customer is on the cut-off list, the higher the fee becomes. In those cases, the amount shown in the graph is for first offenders. Additionally, four of the utilities charge a separate disconnect fee and reconnect fee. In those cases, the graph represents the combined total of both fees. Finally, two additional utilities charge a cut-off fee per service. In those cases, the graph assumes all services are being disconnected.
Cut-off or reconnect fees charged by the 129 utilities range from $13.00 to $550.00 as shown below:
Of the 129 utilities that cut off for non-payment, 94 of them (representing 72.9%) assess the cut-off fee as soon as the cut-off list leaves the office. The percentage of utilities charging the cut-off fee immediately is up 8.5% from the 2019 Utility Fee Survey:
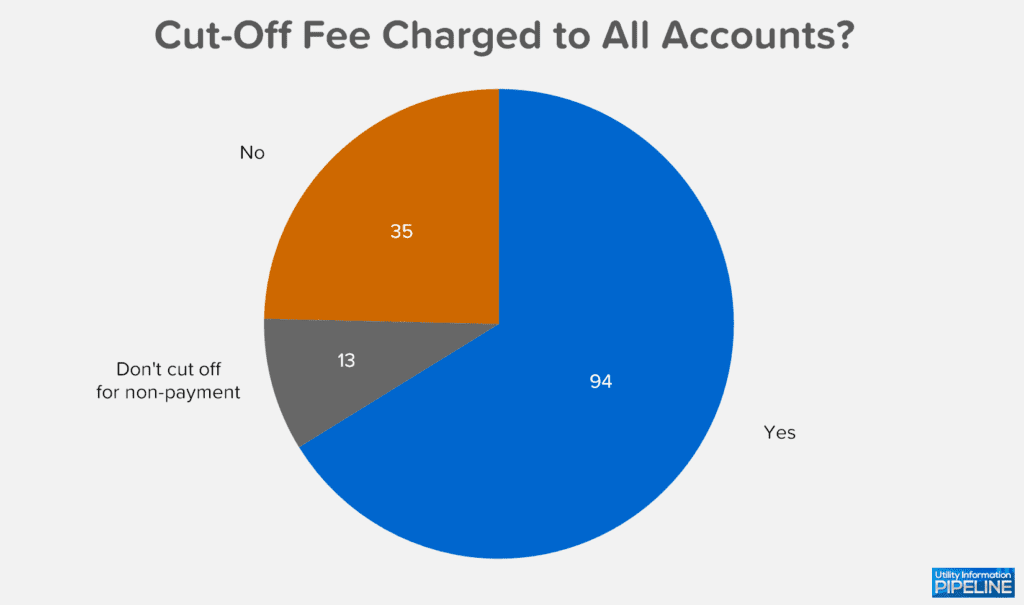
Cut-off fee terminology
As utilities adopt the best practice of charging the cut-off fee as soon as the cut-off list leaves the office, many are finding that terms such as “cut-off fee”, “disconnect fee” or “reconnect fee” are becoming outdated. For that reason, the survey asked what each utility calls its cut-off fee. The results are displayed in the following chart:
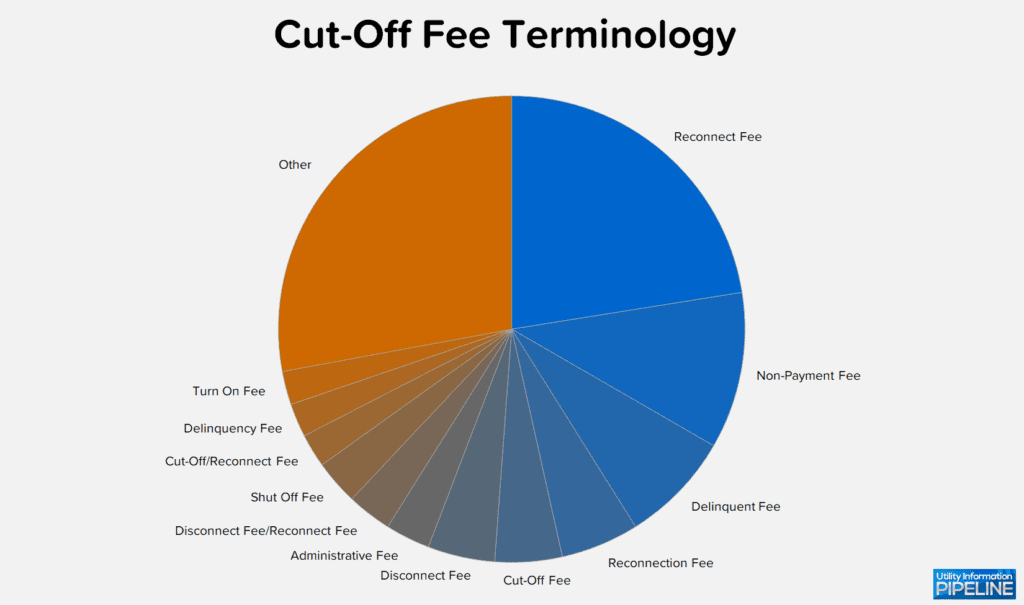
For the number of responses, including the 36 terms included in the “other” category, please click here.
Again this year, Reconnect Fee is still the most popular term, but Non-Payment Fee and Delinquent Fee have become the second and third most popular term, as many utilities adopt terms that do not refer to cut-off or reconnection. Calling your cut-off fee Non-Payment Fee, Delinquent Fee, Service Fee, or any of the other terms not implying cut-off or reconnection helps to avoid the inevitable arguments with customers who must pay the fee but have not been cut off.
As with late fees, the survey also asked how, other than the utility bill, customers are notified that they are about to be cut-off for non-payment. The responses are shown below (again, the total of all responses is greater than the number of participating utilities because some utilities use multiple methods of contact):
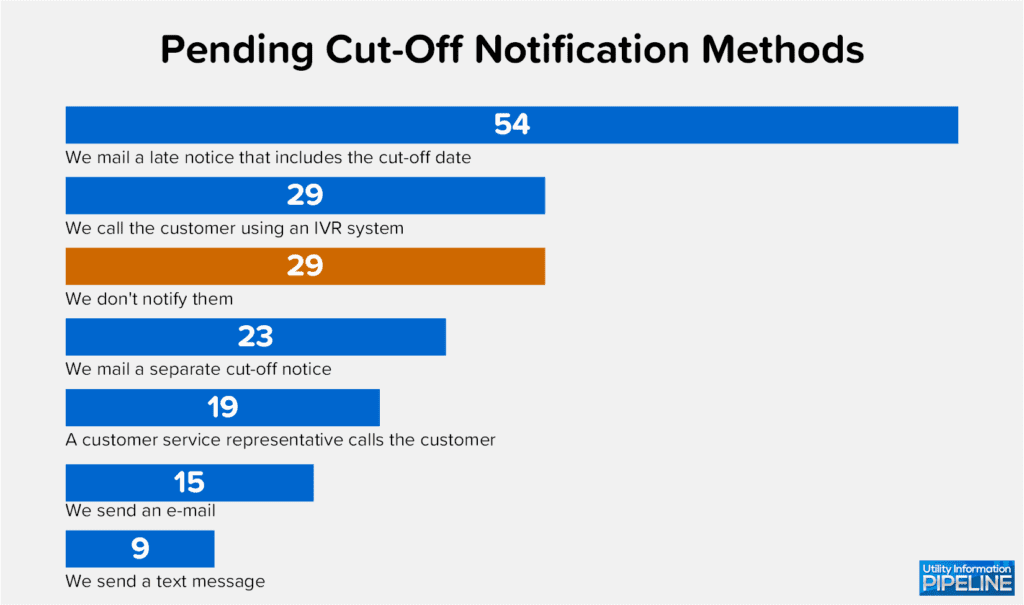
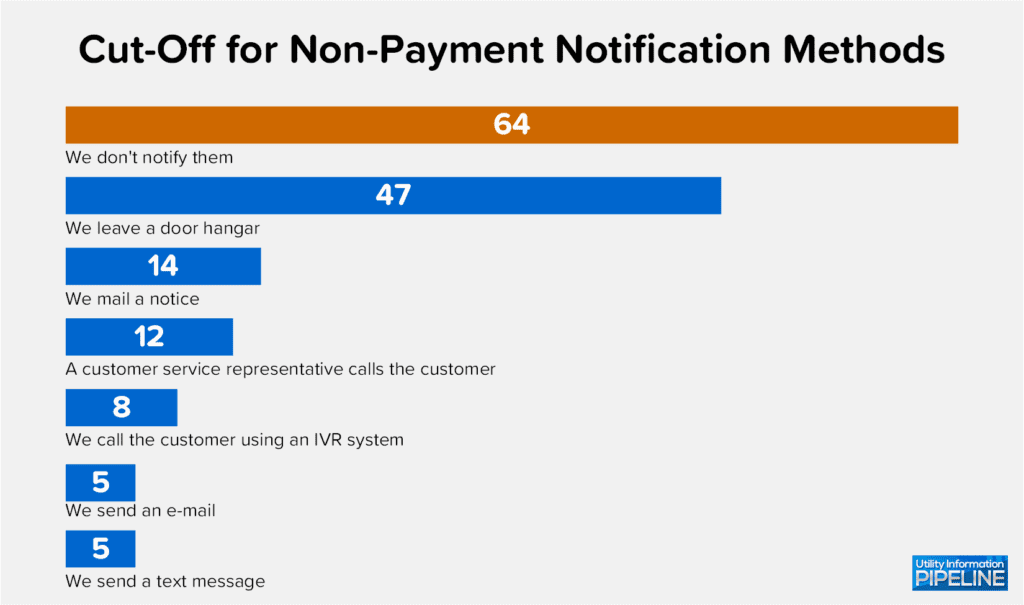
This year’s survey also asked how utilities notify customers after they have been disconnected for non-payment. The responses are shown below (again, a few of the participating utilities employ multiple methods of contact):
After hours reconnect fees
Of the 129 utilities that cut off for non-payment, 58 of them (representing 45.0%) will reconnect after hours and charge a fee for this service. This is down from 51.7% of responding utilities in the 2019 Utility Fee Survey. 46 of the 58 utilities (or 79.3%) will reconnect anytime after regular office hours. The remaining 12 utilities will only reconnect during selected time periods as shown below:
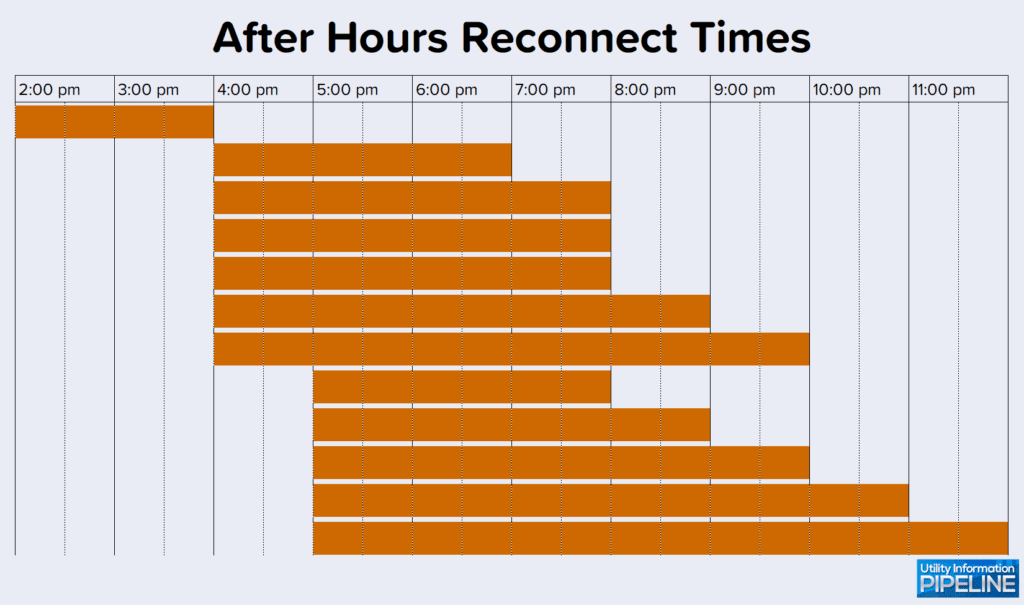
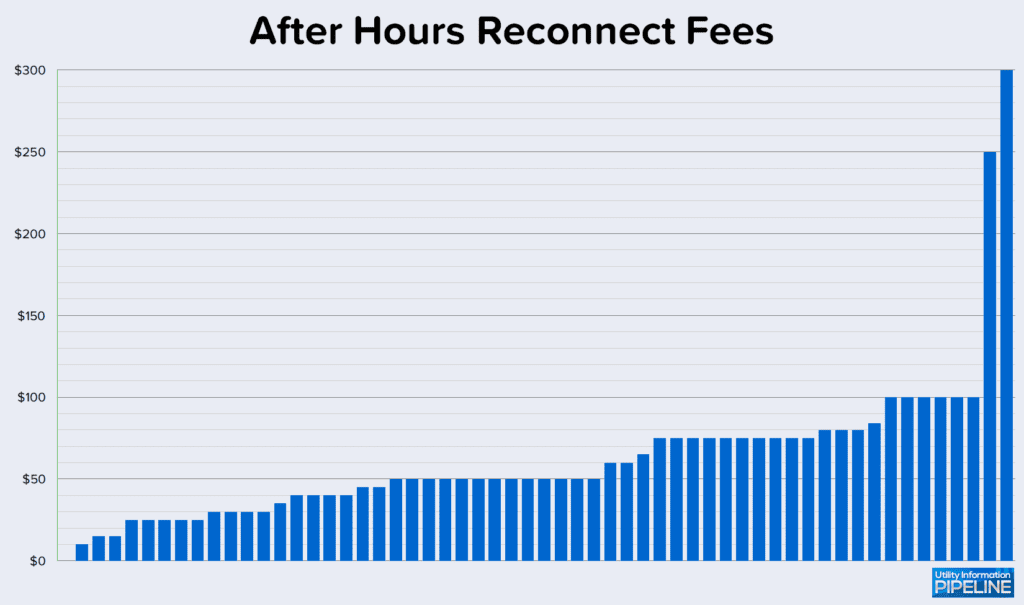
After hours reconnect fee amounts range from no additional charge to $300.00 as shown by the following graph:
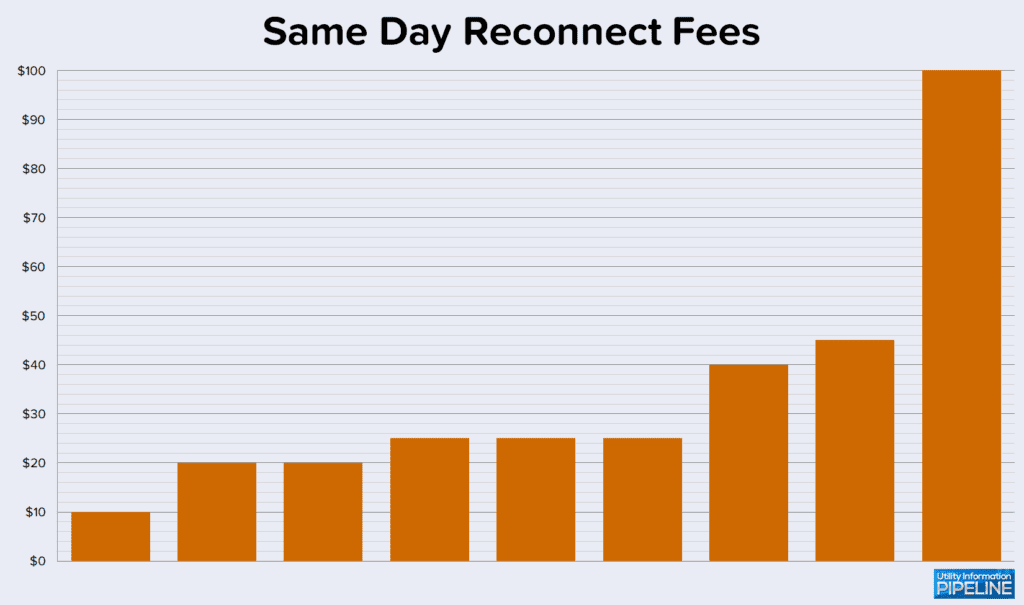
Same day reconnect fees
A new question in this year’s survey asked how many utilities charge a fee for same-day reconnection for non-payment. Nine utilities charge a fee for this service, ranging from $10.00 to $100.00, as shown below:
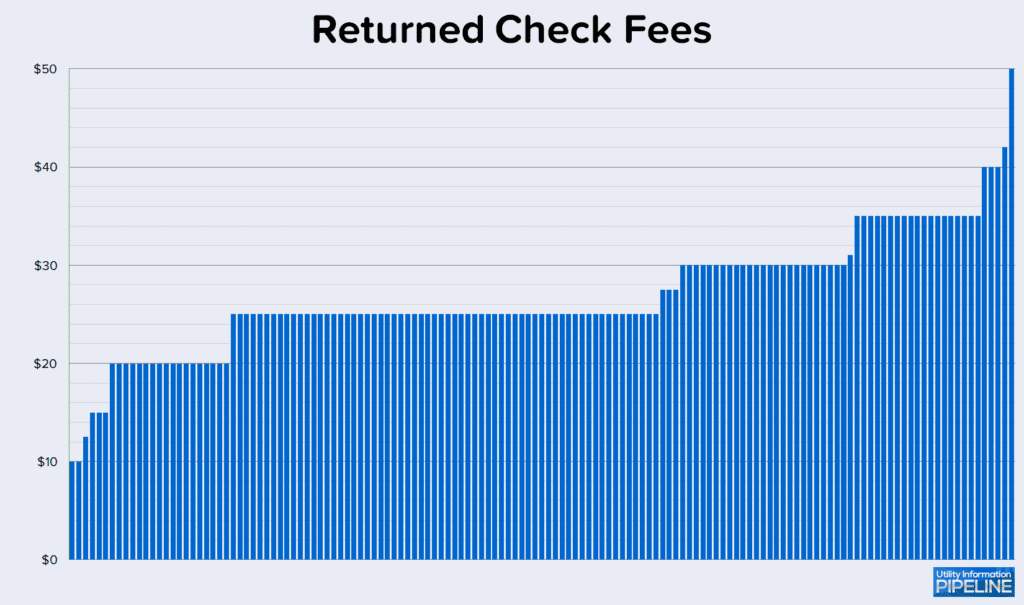
Returned check fees
All 142 participating utilities charge a returned check fee ranging from $10.00 to $50.00, as this graph illustrates (clicking on any of the graphs will open a larger image in a new window):
Interestingly, only 73 (or 51.4%) of the responding utilities charge the maximum fee allowed by their state. 33 utilities (representing 23.2%) charge more than the maximum allowed and 36 (or 25.4%) charge less than the maximum allowed.
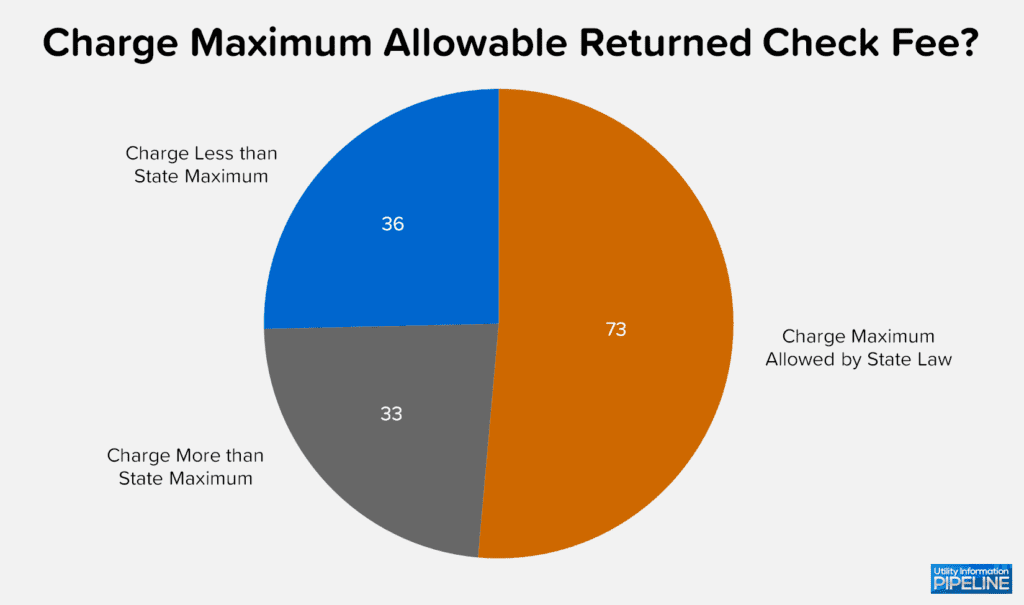
If you’re interested in seeing how your fee compares to the maximum allowed for your state, here is a table with all 50 states.
Application fees
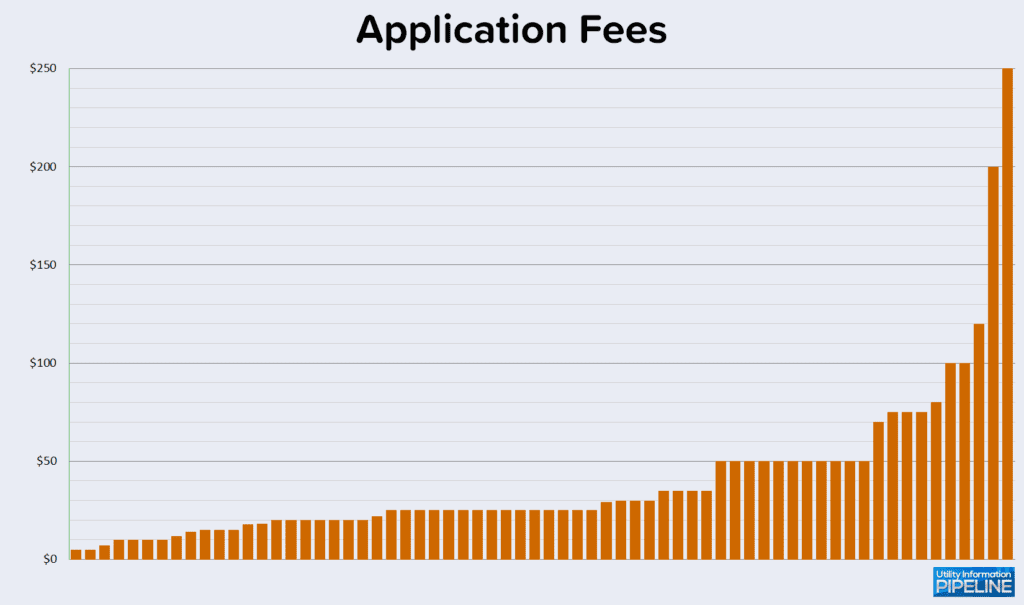
In one of the earliest Utility Information Pipeline issues, I wrote about application for service best practices. One of my recommendations was to charge a non-refundable application fee, in addition to any security deposit, to all new accounts. This year, 66 of the 142 utilities (representing 46.5%) responding to the survey charge such an application or administrative fee. This is the lowest percentage reported since the beginning of the Utility Fee Survey, down from 50.4% in 2019, 47.9% in 2017, 51.9% in 2015, and 52.3% in 2012. These application fees range from $5.00 to $250.00 as shown below:
Transfer fees
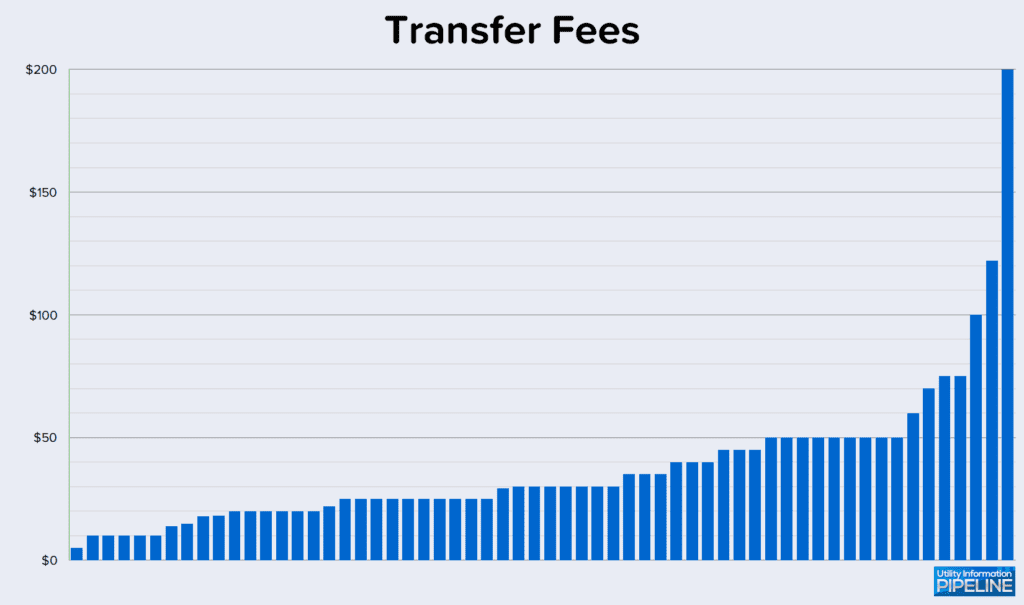
The Utility Fee Survey also asked how much utilities charge as a transfer fee for transferring service from one account to another. 60 of the 142 utilities (representing 42.3%) charge a transfer fee ranging from $5.00 to $100.00. This is down from 45.9% in 2019. Transfer fees charged by the responding utilities are shown in this graph:
Meter reread fees
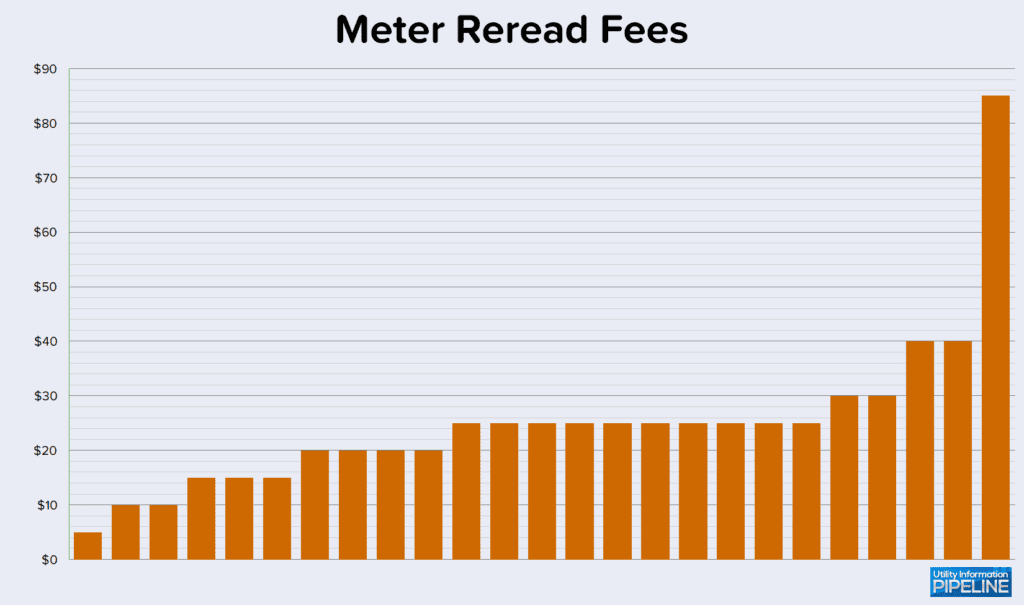
25 of the 142 utilities (or 17.6%) charge a meter reread fee if the customer requests their meter be reread. This is down from 23.0% in 2019, 23.7% in 2017 and 23.6% in 2015. In many cases, this fee is waived if it turns out the customer was correct and the utility misread the meter. Of the utilities that charge a meter reread fee, the fee ranges from $5.00 to $85.00 as this graph shows:
Meter tampering fees
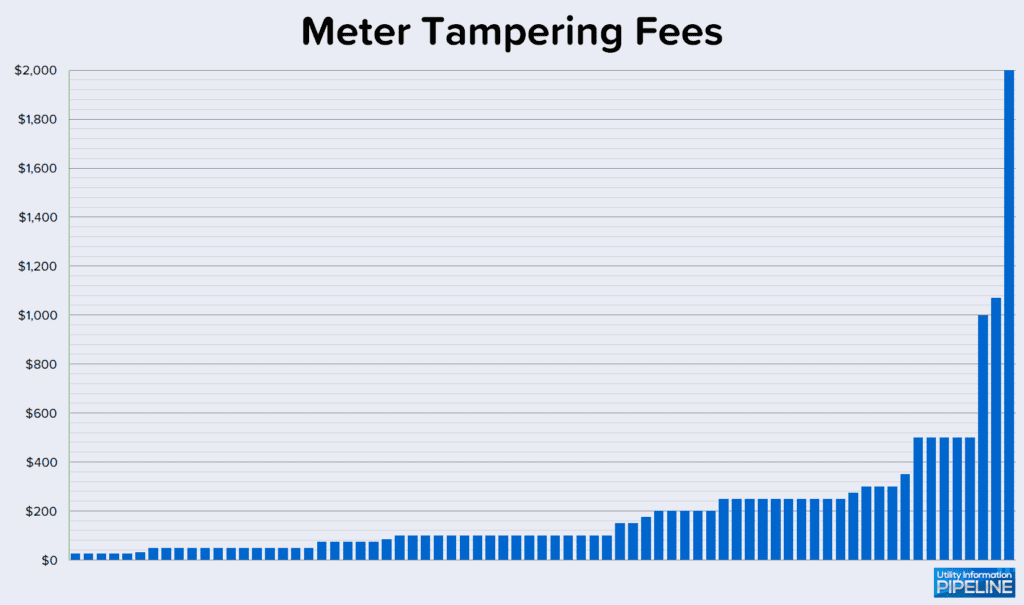
94 of the 142 utilities (or 68.3%) charge a meter tampering fee. This is down from 73.3% in 2019, 77.1% in 2017, and 73.6% in 2015, but up from 60.2% in 2012. Fourteen utilities charge the actual cost of repairs or cost plus an administrative fee. Five additional utilities recovers their costs through the judicial system. Seven utilities have an escalating fee that increases with each meter tampering offense. The remaining 73 utilities charge a flat fee ranging from $25.00 to $2000.00 as shown below:
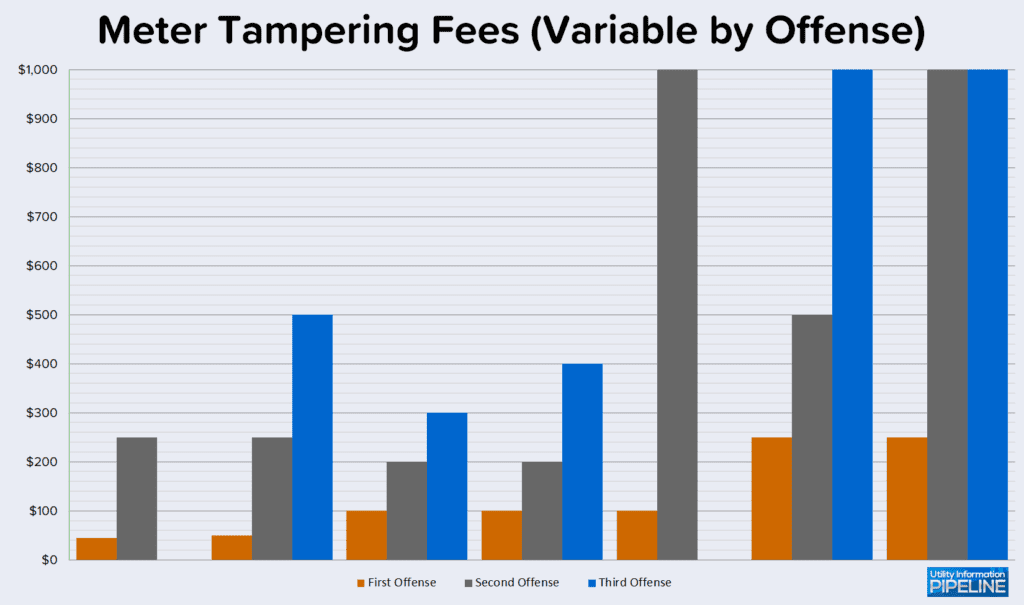
Of the seven utilities that charge an escalating fee, here are the charges for the first, second, and third offenses:
Convenience fees
One of my earliest issues explained why I believe utilities should accept credit cards. Of the 142 utilities responding to the survey, 135 of them (or 95.1%) accept credit cards. This is an increase from 90.4% in 2019, 89.0% in 2017, 81.1% in 2015, and 62.5% in 2012. Clearly, credit card acceptance has become standard practice for most utilities.
Of the 135 that do accept credit cards, 104 (or 77.0%) of these charge a convenience fee as show below:
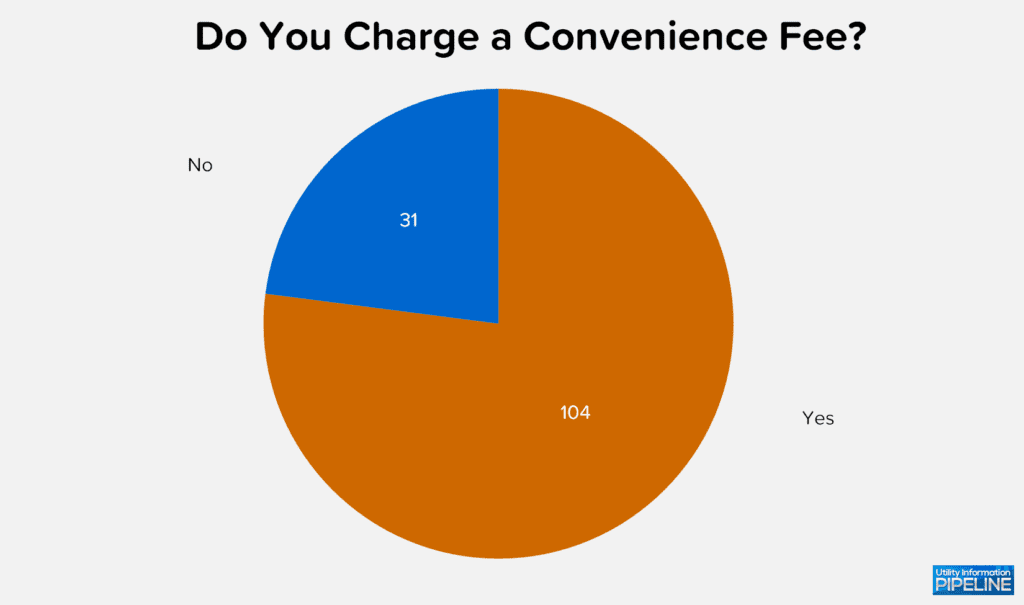
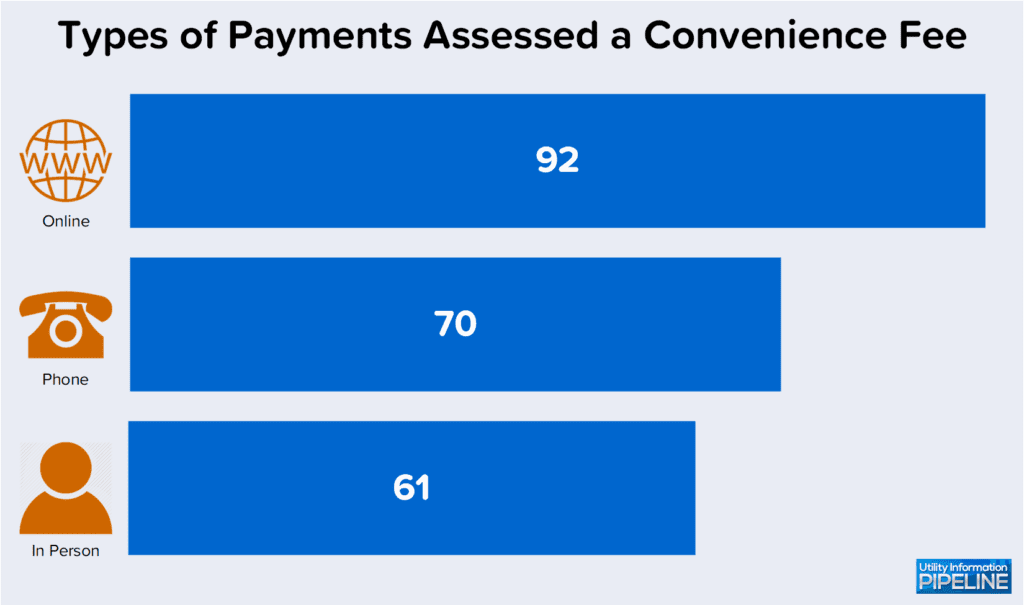
Below is a graphic depicting which methods of credit card payments are assessed convenience fees:
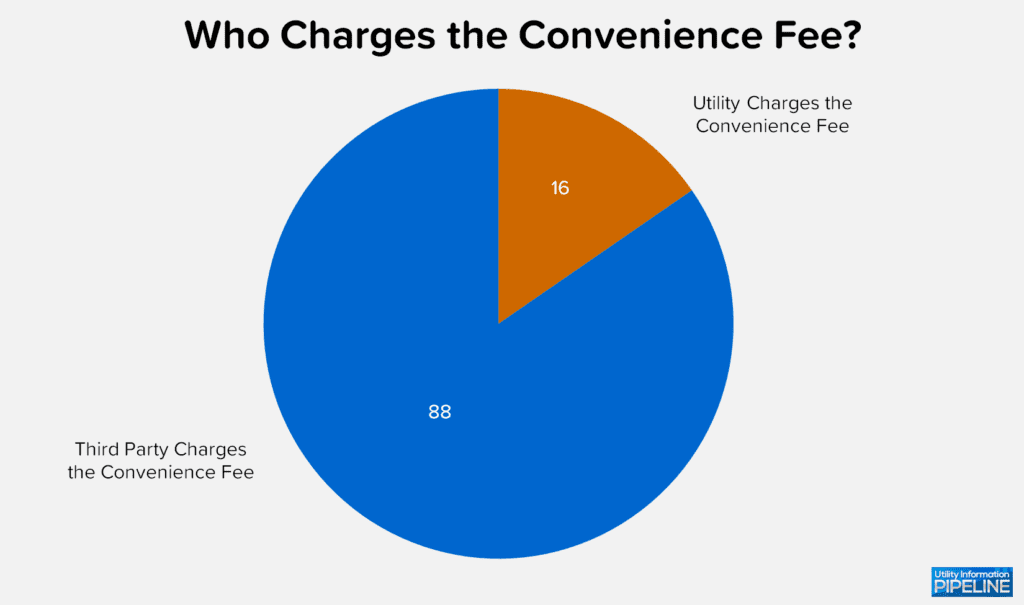
This is the second year the survey asked if the convenience fee is charged by the utility or by a third party. Of the 104 utilities that charge a convenience fee, 88 (or 84.6%) are charged by a third party as shown below. This is up from 81.2% in 2019 and 69.4% in 2017.
The convenience fees charged by these utilities are too diverse in how they are assessed to be graphed, so they are presented here in a table.
Other fees
In addition to the fees that have been described in the three results issues, the survey asked what other fees utilities charge. Below I’ve listed a few of the more creative fees that were reported:
Meter test or calibration fee
At least 14 utilities charge a fee if the customer requests that their meter be tested or calibrated. The survey didn’t specifically ask about meter test fees however, most only charge the fee if the test results validate that the meter is registering correctly.
Return trip fee
When turning a meter on, most utilities will not leave the water on if the meter indicates water is running inside the house and no one is home. This requires the utility to make a return trip when the customer is home to turn the meter on again. Several utilities charge a return trip fee or running water fee to cover the time and expenses involved in returning to the customer’s home.
Field collection fee
Most utilities have adopted the best practice of not collecting money in the field on cut-off day. Two utilities still allow customers to pay the field technician to avoid being cut off and they charge an additional $25.00 or $30.00 to provide that service.
Does your fee schedule need reviewing?
If you think your fee schedule needs to be updated, please give me a call at 919-673-4050 or e-mail me at gary@utilityinformationpipeline.com to learn how fee review could help.